Discover how do i charge a hybrid car with our detailed guide. Learn about charging methods, benefits, tips, and maintenance to maximize your hybrid vehicle’s performance.
Introduction
As the automotive industry evolves, hybrid cars have emerged as a popular choice for environmentally conscious drivers looking for a balance between fuel efficiency and performance. Charging a hybrid car may seem daunting to new owners, but understanding the process can help you make the most of your vehicle’s capabilities. This blog post will answer the question, “How do I charge a hybrid car?” while providing insights into the types of hybrid vehicles, charging methods, benefits, and tips for maintaining your hybrid battery.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to charge your hybrid car effectively and efficiently, ensuring you enjoy all the advantages of this innovative technology.
Understanding Hybrid Cars
Before diving into the charging process, it’s essential to grasp the different types of hybrid vehicles available today:
Types of Hybrid Cars
- Mild Hybrids:
- Use a small electric motor to assist the gasoline engine.
- Cannot be charged from an external source.
- Operate primarily on gasoline but improve fuel efficiency.
- Full Hybrids:
- Can run on an electric motor, a gasoline engine, or a combination of both.
- Regenerative braking captures energy to recharge the battery.
- May be charged using an external power source.
- Plug-in Hybrids (PHEVs):
- Feature a larger battery than full hybrids.
- Can be charged from an external outlet or charging station.
- Offer a greater electric-only driving range.
Understanding your vehicle type will determine how you charge it and the available charging options.
How Do I Charge a Hybrid Car?
1. Charging Methods
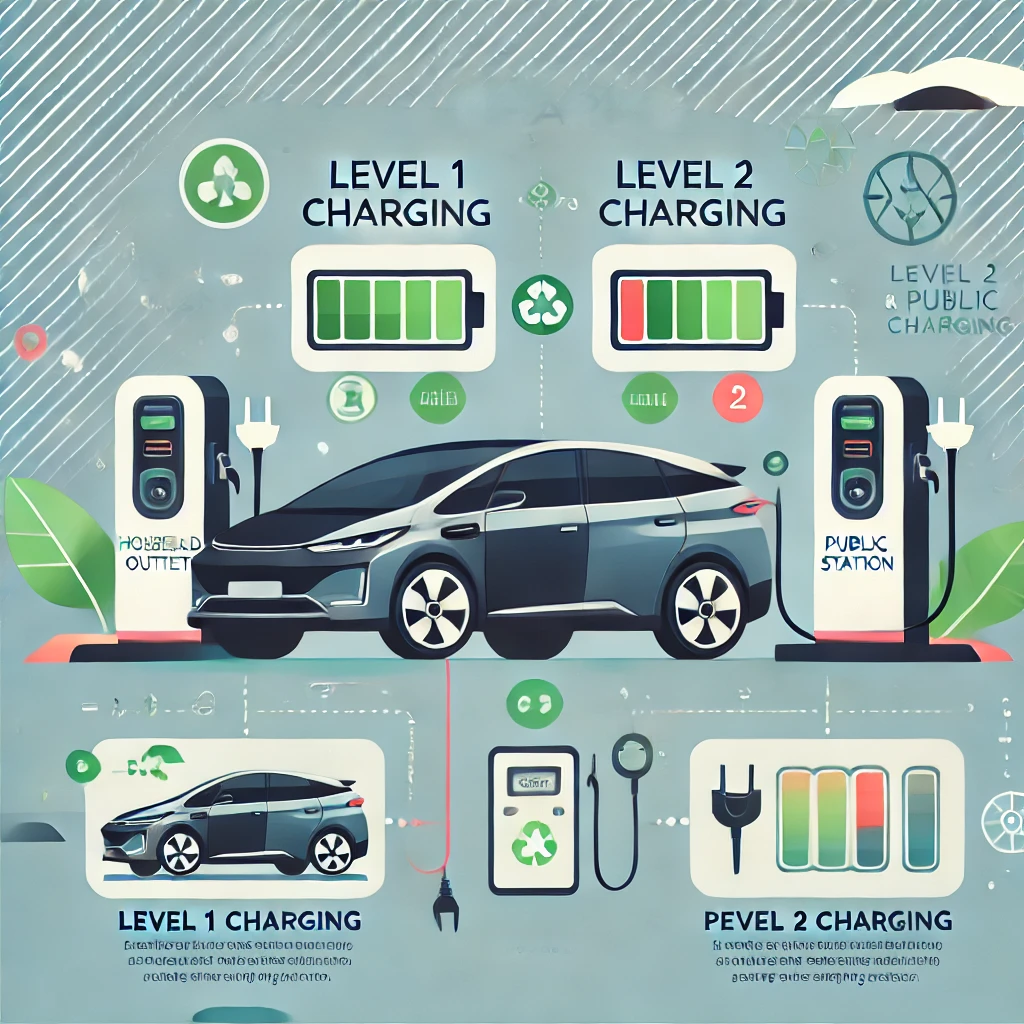
A. Using a Standard Household Outlet
- Level 1 Charging:
- Plug your hybrid car into a standard 120V outlet using the charging cable provided with your vehicle.
- This method is the most convenient for overnight charging but is the slowest, typically providing 3-5 miles of electric range per hour.
B. Public Charging Stations
- Level 2 Charging:
- Utilizes a 240V outlet, significantly speeding up the charging process.
- Public charging stations are often found in parking lots, shopping centers, and gas stations.
- Expect to gain about 10-20 miles of electric range per hour.
C. Fast Charging Stations
- DC Fast Charging:
- Primarily designed for fully electric vehicles, some plug-in hybrids may also use these stations.
- Capable of charging the battery to 80% in about 30 minutes.
- Availability may be limited, and costs may vary by location.
2. Charging Steps for Plug-in Hybrids
- Locate a Charging Station:
- Use apps like PlugShare or ChargePoint to find nearby charging stations.
- Connect the Charging Cable:
- Open the charging port on your hybrid vehicle.
- Attach the charging connector securely to the port.
- Start the Charging Process:
- Follow the station’s instructions, which may involve swiping a card or using a mobile app.
- Ensure the charging status indicator on your vehicle shows it’s charging.
- Monitor Charging:
- Most hybrids have a display that shows the current battery level and charging status.
- Keep an eye on the charging time and battery percentage.
- Unplug and Store:
- Once fully charged, disconnect the cable and store it properly.
- Close the charging port securely.
3. Charging Steps for Full Hybrids
For full hybrids, charging from an external power source is typically unnecessary, as the vehicle recharges its battery through regenerative braking and the gasoline engine. However, if your full hybrid allows external charging, follow similar steps as outlined for plug-in hybrids.
Benefits of Charging a Hybrid Car
Charging your hybrid car has several benefits, enhancing your driving experience and contributing to a greener environment:
1. Cost Savings
- Reduced Fuel Consumption:
- Using electric power for short trips can lower gasoline expenses.
- Tax Incentives:
- Many governments offer tax credits or rebates for hybrid car owners, which can offset initial costs.
2. Environmental Impact
- Lower Emissions:
- Hybrid vehicles emit fewer greenhouse gases than traditional gasoline cars.
- Reduced Dependence on Fossil Fuels:
- Utilizing electric power helps conserve fossil fuel resources.
3. Performance and Efficiency
- Regenerative Braking:
- Captures energy during braking to recharge the battery, improving overall efficiency.
- Enhanced Driving Range:
- Combining electric and gasoline power extends the driving range compared to purely electric vehicles.
Tips for Maintaining Your Hybrid Battery
Maintaining your hybrid battery is crucial for ensuring long-term performance and efficiency. Here are some essential tips:
1. Regular Charging
- Don’t Let the Battery Deplete:
- Regularly charge your hybrid to avoid deep discharging, which can damage the battery.
2. Use the Right Charging Equipment
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines:
- Always use the charging cable provided by the manufacturer to avoid compatibility issues.
3. Monitor Battery Health
- Check Battery Status:
- Regularly monitor your hybrid’s battery health through the vehicle’s diagnostic system.
4. Keep Your Hybrid Clean
- Avoid Dirt and Debris:
- Ensure the charging port and connectors are clean and free from debris to maintain proper connections.
5. Schedule Regular Maintenance
- Follow the Manufacturer Maintenance Schedule:
- Regularly scheduled maintenance checks can help identify potential issues with the hybrid system before they become significant problems.
Conclusion
How do I charge a hybrid car may seem intimidating, but it’s a straightforward process once you understand the different charging methods available. Whether you own a plug-in hybrid or a full hybrid, knowing how to charge your vehicle effectively is essential for maximizing its performance, efficiency, and lifespan.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your hybrid car remains charged and ready to deliver an eco-friendly driving experience. The benefits of hybrid vehicles extend beyond just fuel savings—they play a crucial role in reducing emissions and promoting a more sustainable future.