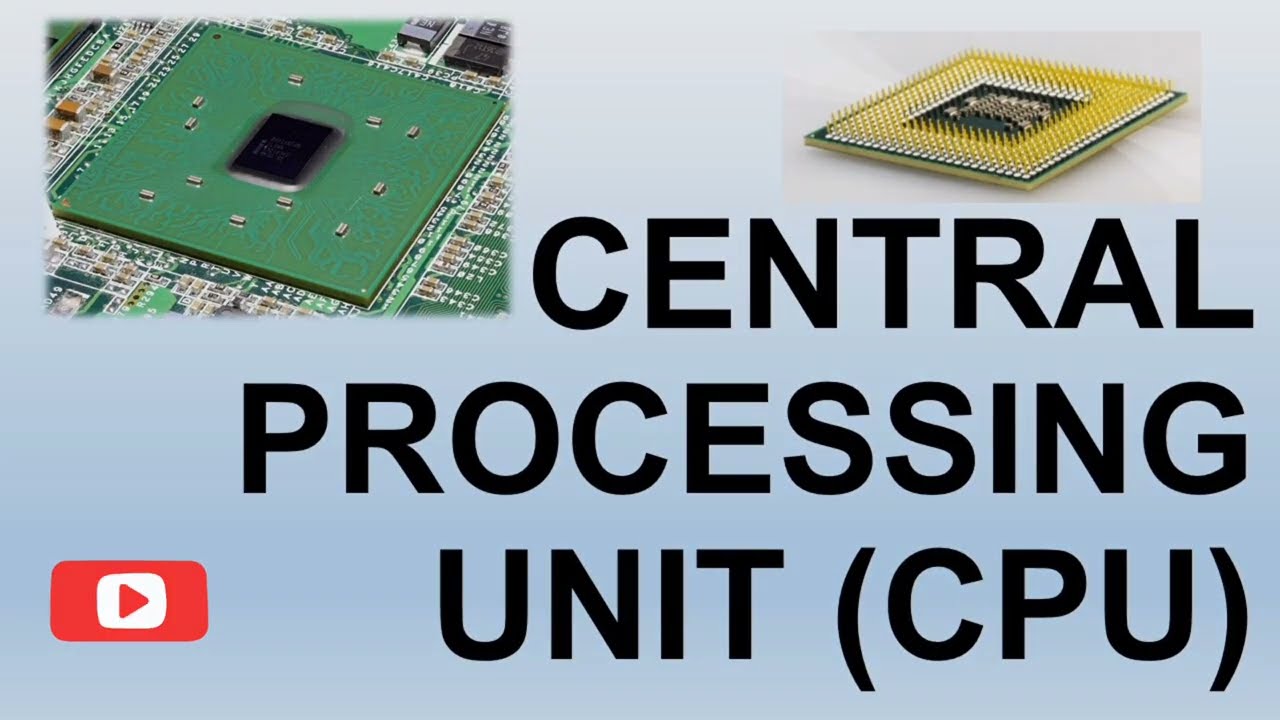
In advancement and computing, the term “CPU Meaning” regularly takes center organization. Whether you’re building a custom PC, selecting the best tablet, or fundamentally endeavoring to comprehend the interior workings of the contraptions we utilize day by day, understanding what a CPU is and its reason is significant. As the brain of each computer, the Central Planning Unit (CPU) plays a noteworthy portion in each progressed handle. In this article, we will dive significantly into the meaning of a CPU, how its capacities, its importance, and the differing sorts open in today’s market.
What is a CPU Meaning?
The Central Dealing Unit (CPU Meaning) is the basic component of a computer that performs most of the dealing with inside a system. It interprets and executes edifying from the computer’s hardware and program, making it reliable for carrying out the operations of a program. In substance, the CPU is the heart of the computer, changing inputs into noteworthy yields by taking after calculations and performing calculations.
The CPU works utilizing twofold code—a course of action of ones and zeros that talk to enlightening, data, and exercises. This enables the CPU to handle assignments such as number-crunching calculations, coherent operations, control signals, and input/output (I/O) handling.
Key Components of a CPU
A CPU is composed of a few humbler parts that work together to execute assignments. Let’s break down these essential components:
1. Control Unit (CU)
The Control Unit arranges the operation of the CPU by getting, translating, and executing instructions from the system’s memory. It acts as the boss of the CPU, ensuring each component works together efficiently.
2. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
The ALU handles all the numerical and steady operations inside the CPU. The ALU takes charge of these capacities at any point you perform a calculation or a coherent comparison. Operations consolidate development, subtraction, increment, division, and decision-making based on comparison.
3. Registers
Registers are small, fast memory zones interior the CPU that store brief data in the midst of planning. Registers are essential for speeding up the by and dealing with time by holding information close to the CPU for quick access.
4. Cache Memory
The cache memory is a small, high-speed memory range that stores as frequently as conceivable utilized instructive data. This licenses the CPU to get to essential information without going back to the essential system memory (Hammer), basically advancing planning efficiency.
How Does a CPU Work?
A CPU works by taking after the fetch-decode-execute cycle. Here’s a breakdown of each stage:
1. Fetch
In this arrangement, the Control Unit brings the instruction from the system’s Crush (Unpredictable Get to Memory). These illuminations are put absent in memory ranges called addresses, and the CPU recuperates them to get ready for the needed task.
2. Decode
After getting the instruction, the CPU interprets it. The instruction is changed over into a clear shape, allowing the CPU to get it the movement it needs to take. The Control Unit deciphers the operation and plans the components involved.
3. Execute
Once decoded, the CPU moves to the execution arrangement, where it performs the action coordinated by the instruction. The CPU handles the operation efficiently, whether it’s performing a calculation, moving data, or communicating with other gear components.
4. Store
In a few cases, the final orchestrate incorporates putting the result of the operation back into the system’s memory for future use.
Why is the CPU Important?
The CPU is imperative since it controls and arranges all of the computer’s capacities. Without a CPU, a computer is fundamentally pointless. It is the component that ensures that all shapes are executed effectively, from the fundamental opening of a web browser to running complex simulations.
Moreover, the CPU’s execution impacts a computer’s speed and capability. Speedier CPUs can handle more errands at once, making them significant for clients who require high-performance systems, such as gamers, video editors, and data examiners. For common clients, having a strong CPU infers speedier boot times, speedier application dispatches, and smoother multitasking.
Types of CPUs
Over a long time, CPUs have progressed through and through, and there are distinctive sorts available depending on the needs of the client. A few of the crucial sorts include:
1. Single-Core CPU
Single-core CPUs were the to start with to be made and can as it were execute one instruction at a time. While this sort is directly for the most part out of date, they were foundational to the change of cutting-edge CPUs.
2. Dual-Core CPU
A dual-core CPU contains two processors interior the same CPU, allowing for predominant multitasking and advanced execution compared to single-core models. Dual-core CPUs are predominant in budget and mid-range computers.
3. Quad-Core and Octa-Core CPUs
As demands for higher execution extended, quad-core (four processors) and octa-core (eight processors) CPUs were made. These models can handle more concurrent assignments, making them idealize for gaming, video rendering, and capable applications.
4. Hyper-Threading Technology
Some CPUs highlight hyper-threading advancement, which grants a single center to handle various strings (assignments) at once. This effectively sets the number of errands the CPU can handle, making strides in multitasking without the requirement for additional physical cores.
Factors Affecting CPU Performance
Several components choose the execution of a CPU:
1. Clock Speed
Clock speed, measured in GHz (gigahertz), implies how many cycles per minute the CPU can execute. A higher clock speed suggests the CPU can perform more assignments in a shorter time.
2. Core Count
The number of centers in a CPU chooses how various shapes can be executed at the same time. More centers regularly result in prevalent execution for multitasking and resource-intensive applications.
3. Cache Size
A greater cache memory licenses the CPU to store more edifying closer to the planning unit, moving forward speed and efficiency.
4. Power Consumption and Heat
CPUs with higher execution habitually eat up more control and create more warmth. It’s imperative to consider cooling systems, such as warm sinks and fans, to keep up the perfect execution of high-end CPUs.
Choosing the Right CPU
When selecting a CPU, it’s fundamental to consider your specific needs. Gamers, substance creators, and specialists requiring tall computing control should see for multi-core CPUs with tall clock speeds and sweeping caches. For casual clients, a budget-friendly CPU with coordinated execution may be more than adequate for normal errands like web browsing, mail, and office applications.
Conclusion
Understanding the CPU meaning and functions is fundamental to choosing the right computer system and maximizing performance. The CPU acts as the brain of your device, ensuring that every operation, from basic tasks to high-level calculations, is executed smoothly. Whether you’re building a gaming rig, a professional workstation, or a simple home PC, selecting the correct CPU will determine the efficiency and power of your system.